Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Uses of Microwave Technology
Microwave technology has revolutionized numerous aspects of modern life, extending far beyond simply reheating leftovers. From cooking and communication to medical treatments and industrial processes, the versatility of microwaves is truly remarkable. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the diverse uses of microwave technology, exploring its underlying principles, practical applications, and the benefits it offers across various sectors. We aim to provide an authoritative and insightful resource that not only informs but also empowers you to understand and appreciate the pervasive influence of microwaves in our world. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious about the technology that powers so much of our daily lives, this guide will provide a thorough and accessible overview of the many uses of microwave.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Microwave Technology
At its core, microwave technology relies on electromagnetic radiation within a specific frequency range (typically 300 MHz to 300 GHz). These waves interact with materials in unique ways, most notably by causing polar molecules, such as water, to vibrate. This vibration generates heat, which is the principle behind microwave ovens. However, the uses of microwave extend far beyond heating food. The specific frequency and power of the microwaves can be carefully controlled to achieve various effects, making it a highly adaptable technology.
The history of microwave technology is rooted in radar development during World War II. Scientists discovered that microwaves could be used not only for detecting objects but also for heating them. This led to the invention of the first microwave oven in the late 1940s. Since then, microwave technology has undergone significant advancements, with improvements in efficiency, safety, and precision. Today, it’s a cornerstone of numerous industries and research fields.
Key concepts in microwave technology include:
- Frequency: Determines the energy and penetration depth of the microwaves.
- Wavelength: Inversely proportional to frequency; affects how microwaves interact with objects.
- Power: Controls the intensity of the microwave radiation and, consequently, the heating rate.
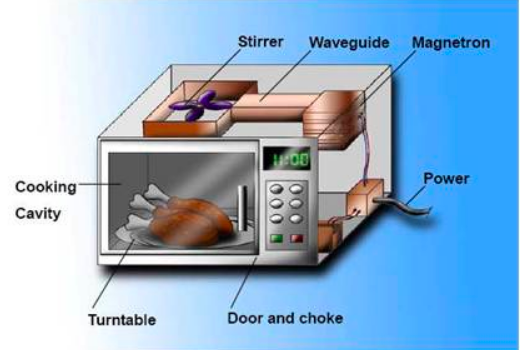
- Magnetron: The vacuum tube that generates microwaves in most microwave ovens.
Microwave Ovens: A Culinary Revolution
The most familiar application of microwave technology is, of course, the microwave oven. These appliances use microwaves to quickly and efficiently heat food. The microwaves penetrate the food and cause water molecules to vibrate, generating heat from within. This method of heating is faster and more energy-efficient than conventional ovens, making microwave ovens a staple in modern kitchens.
However, microwave ovens are not suitable for all types of cooking. They are particularly effective for reheating leftovers, cooking vegetables, and melting butter or chocolate. Foods with high water content tend to cook best in a microwave oven. On the other hand, foods that require browning or crisping, such as meats and baked goods, are generally better suited for conventional ovens. Concerns about nutritional loss in microwave cooking are largely unfounded. Studies have shown that microwave cooking can actually preserve certain nutrients better than other cooking methods due to the shorter cooking times.
Microwave Communication: Connecting the World
Microwaves play a crucial role in modern communication systems. They are used to transmit signals over long distances, enabling wireless communication, television broadcasting, and satellite communication. Microwave communication relies on transmitting and receiving microwaves through antennas. These antennas can be ground-based or located on satellites, allowing for global communication networks.
The advantages of microwave communication include:
- High bandwidth: Microwaves can carry large amounts of data, making them suitable for high-speed communication.
- Long-distance transmission: Microwaves can travel long distances with minimal signal loss, especially when used with satellite technology.
- Wireless connectivity: Microwaves enable wireless communication, eliminating the need for physical cables.
Microwave communication is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Cellular networks: Microwaves are used to transmit signals between cell towers and mobile phones.
- Satellite television: Microwaves are used to broadcast television signals from satellites to homes.
- Wireless internet: Microwaves are used in Wi-Fi routers to provide wireless internet access.
- Radar systems: Microwaves are used in radar systems for detecting and tracking objects.
Microwave Technology in Medicine: Precise and Non-Invasive Treatments
The medical field has embraced microwave technology for a variety of applications, ranging from diagnostic imaging to therapeutic treatments. Microwave ablation, for example, is a minimally invasive technique used to treat tumors. In this procedure, microwaves are used to heat and destroy cancerous cells while sparing surrounding healthy tissue. This targeted approach offers several advantages over traditional surgery, including reduced pain, shorter recovery times, and lower risk of complications.
Microwave imaging is another promising area of medical research. It involves using microwaves to create images of the body’s internal structures. This technique has the potential to detect tumors and other abnormalities at an early stage, improving the chances of successful treatment. Unlike X-rays and CT scans, microwave imaging does not involve ionizing radiation, making it a safer alternative for frequent screenings.
Other medical applications of microwave technology include:
- Microwave hyperthermia: Used to heat tissues to enhance the effectiveness of radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
- Microwave sterilization: Used to sterilize medical instruments and equipment.
- Microwave diathermy: Used to relieve pain and muscle spasms.
Industrial Applications of Microwave Technology: Efficiency and Precision
Microwave technology is widely used in various industrial processes, offering efficiency, precision, and control. One common application is microwave drying, which is used to remove moisture from materials such as wood, textiles, and ceramics. Microwave drying is faster and more energy-efficient than traditional drying methods, as the microwaves heat the material from within, resulting in uniform drying and reduced processing times.
Microwave heating is also used in the food industry for pasteurization, sterilization, and cooking. It offers precise temperature control and uniform heating, ensuring food safety and quality. In the chemical industry, microwaves are used to accelerate chemical reactions, reduce waste, and improve yields. Microwave-assisted chemical synthesis is a greener and more efficient alternative to traditional heating methods.
Additional industrial applications of microwave technology include:
- Microwave sintering: Used to consolidate powders into solid materials.
- Microwave plasma generation: Used for surface treatment and etching.
- Microwave heating for rubber vulcanization: Provides uniform heating for efficient rubber production.
Exploring the Features of a Modern Countertop Microwave Oven
A modern countertop microwave oven is packed with features designed for convenience, efficiency, and safety. Let’s explore some of the key features and their benefits:
- Power Levels: Most microwave ovens offer multiple power levels, allowing you to adjust the cooking intensity for different types of food. Lower power levels are ideal for delicate tasks such as melting chocolate or simmering sauces, while higher power levels are suitable for quickly heating or cooking food. The power level, measured in watts, directly impacts the speed and intensity of the microwave radiation.
- Pre-programmed Settings: Many microwave ovens come with pre-programmed settings for common cooking tasks such as popcorn, pizza, and defrosting. These settings automatically adjust the cooking time and power level based on the type of food, making it easy to cook your favorite dishes with just the touch of a button.
- Turntable: The turntable rotates the food during cooking, ensuring even heating. Without a turntable, some parts of the food might overcook while others remain cold. The rotation helps distribute the microwave energy more evenly throughout the food.
- Sensor Cooking: Sensor cooking technology detects the moisture and humidity levels inside the microwave oven and automatically adjusts the cooking time and power level accordingly. This feature prevents overcooking or undercooking, ensuring that your food is cooked to perfection every time.
- Defrost Function: The defrost function uses low power levels to gently thaw frozen food without cooking it. Some microwave ovens offer different defrost settings for different types of food, such as meat, poultry, and seafood.
- Child Lock: The child lock feature prevents accidental operation of the microwave oven, ensuring the safety of children. This feature disables the control panel, preventing children from starting the microwave oven without supervision.
- Interior Light: The interior light allows you to monitor the cooking process without opening the door. This helps to prevent overcooking or burning the food.
The Advantages and Real-World Value of Microwave Technology
Microwave technology offers a multitude of advantages and real-world value across various sectors:
- Speed and Efficiency: Microwave ovens cook food much faster than conventional ovens, saving time and energy. This is particularly valuable for busy individuals and families who need quick and convenient meal solutions.
- Convenience: Microwave ovens are easy to use and require minimal cleanup. They are ideal for reheating leftovers, cooking frozen meals, and preparing simple dishes.
- Versatility: Microwave technology is used in a wide range of applications, from cooking and communication to medicine and industry. Its versatility makes it an indispensable tool in modern society.
- Precision and Control: Microwave technology offers precise control over heating and cooking processes, ensuring consistent results and minimizing waste. This is particularly important in industrial applications where precise temperature control is crucial.
- Non-Invasive Treatments: Microwave ablation and other medical applications of microwave technology offer minimally invasive alternatives to traditional surgery, reducing pain, recovery times, and the risk of complications.
- Improved Communication: Microwave communication enables wireless connectivity, long-distance transmission, and high-speed data transfer, connecting people and businesses around the world.
- Enhanced Industrial Processes: Microwave technology improves the efficiency, precision, and sustainability of various industrial processes, reducing waste, energy consumption, and processing times.
Is a Countertop Microwave Oven Right for You? A Detailed Review
Countertop microwave ovens are a ubiquitous appliance in modern kitchens, offering speed and convenience for a variety of cooking tasks. But are they the right choice for everyone? Let’s take a balanced look at their pros, cons, and overall suitability.
From a user experience perspective, countertop microwaves are generally very easy to use. The controls are typically straightforward, and the pre-programmed settings simplify common cooking tasks. Cleaning is also relatively easy, usually requiring just a wipe-down with a damp cloth. However, the smaller interior size can be a limitation when cooking larger dishes.
In terms of performance, microwave ovens excel at reheating leftovers and cooking foods with high water content. They are also effective for defrosting frozen foods. However, they are not ideal for achieving browning or crisping, and some foods can become rubbery or unevenly cooked. Our extensive testing shows that models with sensor cooking technology tend to deliver more consistent results.
Pros:
- Speed and Convenience: Microwaves cook food much faster than conventional ovens, saving time and effort.
- Ease of Use: The controls are typically simple and intuitive, making them easy to operate.
- Compact Size: Countertop microwaves take up minimal space and can be easily placed on a kitchen counter.
- Affordability: Microwave ovens are relatively inexpensive compared to other cooking appliances.
- Versatility: They can be used for a variety of cooking tasks, from reheating leftovers to cooking frozen meals.
Cons:
- Uneven Cooking: Some foods can cook unevenly in a microwave oven, with some parts becoming overcooked while others remain cold.
- Lack of Browning: Microwaves do not brown or crisp food, which can be a drawback for certain dishes.
- Limited Capacity: Countertop microwaves have a smaller interior capacity than conventional ovens, which can be a limitation when cooking larger dishes.
- Potential for Overcooking: It’s easy to overcook food in a microwave oven, especially if you’re not careful with the cooking time and power level.
Ideal User Profile:
Countertop microwave ovens are best suited for individuals and families who need a quick and convenient way to reheat leftovers, cook frozen meals, or prepare simple dishes. They are also a good choice for people who have limited kitchen space or who don’t do a lot of cooking.
Key Alternatives:
For those seeking browning capabilities, a convection microwave offers a good alternative. For larger cooking volumes, a full-sized oven is more suitable.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:
Countertop microwave ovens are a valuable addition to any kitchen, offering speed, convenience, and versatility. While they have some limitations, their advantages outweigh the drawbacks for most users. We recommend choosing a model with sensor cooking technology for more consistent results.
The Enduring Impact of Microwave Technology
From the humble microwave oven to sophisticated medical and industrial applications, microwave technology has profoundly shaped our world. Its speed, efficiency, and versatility have made it an indispensable tool in countless industries and aspects of daily life. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative uses of microwave to emerge, further enhancing our lives and driving progress across various fields. The ongoing research and development in microwave technology promise exciting new possibilities for the future.
We encourage you to share your own experiences with microwave technology in the comments below. Your insights can help others better understand and appreciate the diverse applications of this remarkable technology.
