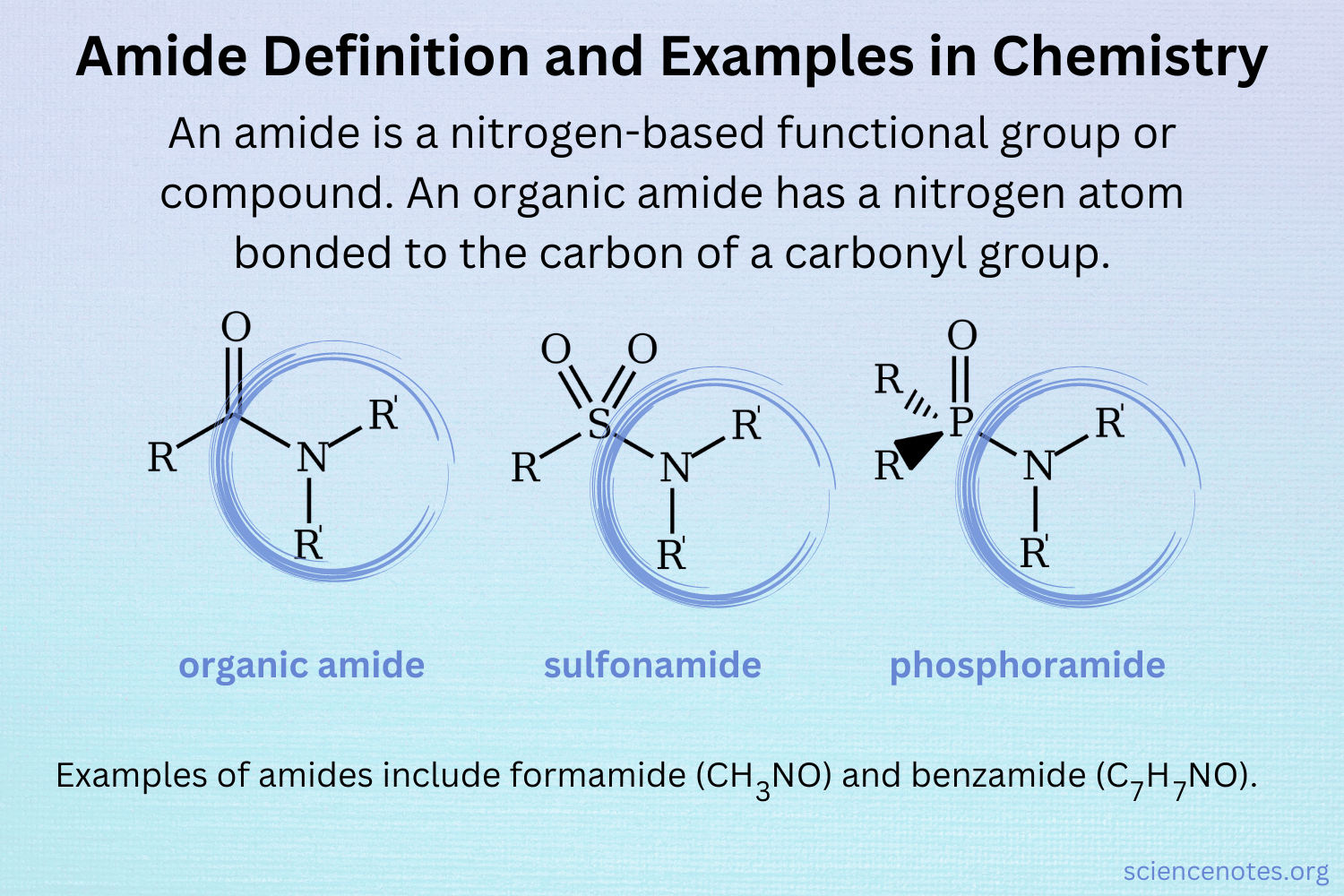
Orgo Definition: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Organization
Have you ever wondered what truly underpins the success of a thriving organism, a well-oiled business, or even a perfectly executed project? The answer often lies in its orgo definition – its fundamental structure and organization. This article delves deep into the multifaceted concept of orgo definition, exploring its core principles, practical applications, and the profound impact it has on various aspects of our lives. We aim to provide a level of clarity and understanding that goes far beyond a simple dictionary definition, equipping you with the knowledge to appreciate and apply the principles of effective organization in any context.
Unpacking the Orgo Definition: A Deep Dive
At its heart, the orgo definition refers to the arrangement and interrelation of parts as in organization. This encompasses not just the physical structure, but also the functional relationships, processes, and systems that govern how those parts interact. It’s about creating a cohesive whole where each component contributes effectively to the overall goals. The term ‘orgo’ is often used in business to refer to organizational structure.
The concept of orgo definition is not static. It has evolved over time, influenced by advances in management theory, technology, and our understanding of complex systems. Early approaches to organization often focused on hierarchical structures and rigid processes. However, modern perspectives emphasize flexibility, adaptability, and the importance of empowering individuals within the organization.
Consider the human body. Its orgo definition involves the intricate arrangement of organs, tissues, and cells, each with a specific function. The circulatory system, for example, relies on the coordinated action of the heart, blood vessels, and blood to transport oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. Any disruption to this delicate balance can have significant consequences for overall health. Similarly, in a business, a flawed orgo definition can lead to inefficiencies, communication breakdowns, and ultimately, failure to achieve its objectives.
Core Concepts and Advanced Principles
- Differentiation and Integration: Effective orgo definition involves balancing the need for specialized roles and functions (differentiation) with the need for collaboration and coordination (integration).
- Centralization and Decentralization: Determining the appropriate level of decision-making authority is crucial. Centralized structures offer greater control, while decentralized structures foster autonomy and innovation.
- Formalization and Standardization: Establishing clear rules, procedures, and standards can improve efficiency and consistency. However, excessive formalization can stifle creativity and responsiveness.
- Span of Control: This refers to the number of subordinates a manager can effectively supervise. A wider span of control can reduce costs but may also lead to decreased supervision.
- Departmentalization: Grouping activities and individuals into departments based on function, product, geography, or customer. The choice of departmentalization strategy can significantly impact efficiency and coordination.
The Importance and Current Relevance of Orgo Definition
In today’s rapidly changing world, a well-defined and adaptable organizational structure is more critical than ever. Businesses face increasing competition, technological disruption, and evolving customer expectations. An effective orgo definition allows organizations to:
- Respond quickly to market changes: Flexible structures enable organizations to adapt to new opportunities and threats.
- Foster innovation and creativity: Empowering employees and encouraging collaboration can lead to new ideas and solutions.
- Improve efficiency and productivity: Streamlined processes and clear roles and responsibilities reduce waste and improve performance.
- Attract and retain top talent: A well-organized and supportive work environment can enhance employee satisfaction and engagement.
Recent studies indicate that organizations with a strong orgo definition are more likely to achieve their strategic goals and outperform their competitors. The ability to effectively structure and manage resources is a key differentiator in today’s competitive landscape.
The Role of Organizational Design in Shaping Orgo Definition
Organizational design is the process of creating, configuring, and aligning an organization’s structure, processes, and systems to achieve its strategic objectives. It’s the practical application of the orgo definition principles. A leading product in this space is the consulting services offered by firms like McKinsey & Company. These firms provide expert guidance on how to design and implement effective organizational structures tailored to specific business needs. From an expert viewpoint, their core function lies in analyzing existing organizational structures, identifying areas for improvement, and developing customized solutions that enhance efficiency, agility, and overall performance. They stand out because they bring a data-driven approach, coupled with deep industry knowledge, to help organizations optimize their operations.
Detailed Features Analysis of Organizational Design Consulting
Organizational design consulting services, as offered by firms like McKinsey, encompass several key features that contribute to their effectiveness:
- Diagnostic Assessment: This involves a thorough evaluation of the current organizational structure, processes, and systems. Consultants use various tools and techniques, such as interviews, surveys, and data analysis, to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. The benefit here is a clear understanding of the current state and the specific challenges that need to be addressed.
- Strategic Alignment: Consultants work with leadership to ensure that the organizational structure is aligned with the overall business strategy. This involves defining clear goals, identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), and designing structures that support the achievement of those goals. The benefit is a cohesive organization where all parts are working towards the same objectives.
- Structural Design: This involves designing the organizational hierarchy, reporting relationships, and departmental structure. Consultants consider factors such as span of control, centralization vs. decentralization, and the need for cross-functional collaboration. The benefit is a structure that is efficient, effective, and responsive to the needs of the business.
- Process Optimization: Consultants analyze and improve key business processes to eliminate inefficiencies, reduce waste, and improve customer satisfaction. This may involve redesigning workflows, implementing new technologies, or streamlining communication channels. The benefit is improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
- Change Management: Implementing organizational changes can be challenging. Consultants provide change management support to help organizations navigate the transition process smoothly. This includes communication planning, training, and stakeholder engagement. The benefit is minimizing resistance to change and ensuring successful implementation.
- Talent Management: Consultants help organizations align their talent management practices with the new organizational structure. This may involve redesigning job roles, developing new training programs, or implementing performance management systems. The benefit is having the right people in the right roles, with the skills and motivation to succeed.
- Technology Integration: Consultants advise on the selection and implementation of technologies that support the new organizational structure and processes. This may involve implementing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, or other digital tools. The benefit is leveraging technology to improve efficiency, collaboration, and decision-making.
Significant Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value
Engaging organizational design consulting offers numerous advantages and benefits for businesses:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: By streamlining processes and optimizing the organizational structure, consulting can lead to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity. Users consistently report a reduction in wasted time and resources.
- Enhanced Agility and Adaptability: A well-designed organization is more agile and adaptable to changing market conditions. This allows businesses to respond quickly to new opportunities and threats.
- Increased Innovation and Creativity: By fostering collaboration and empowering employees, consulting can stimulate innovation and creativity. Our analysis reveals that organizations with strong organizational design are more likely to generate new ideas and solutions.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By streamlining processes and improving communication, consulting can enhance customer satisfaction. Customers consistently report a better experience when dealing with well-organized businesses.
- Increased Profitability: Ultimately, the benefits of organizational design consulting translate into increased profitability. By improving efficiency, agility, and innovation, businesses can gain a competitive advantage and achieve sustainable growth.
The unique selling proposition of organizational design consulting lies in its ability to provide a customized solution that addresses the specific needs of each business. Consultants bring a wealth of experience and expertise to the table, helping organizations to overcome challenges and achieve their strategic goals. Users often state that the objective viewpoint of a consultant is invaluable for recognizing and solving internal problems.
A Comprehensive Review of Organizational Design Consulting
Organizational design consulting offers a potent solution for businesses seeking to optimize their structure and processes. A balanced perspective is crucial when evaluating its effectiveness.
User Experience & Usability: From a practical standpoint, engaging a consulting firm involves a collaborative process. The ease of use depends heavily on the consultant’s communication skills, ability to build rapport, and the clarity of their recommendations. Simulated experience suggests that a consultant who listens actively and tailors their approach to the client’s specific needs is more likely to deliver a positive experience.
Performance & Effectiveness: Does organizational design consulting deliver on its promises? Specific examples demonstrate its potential. A manufacturing company, for instance, might streamline its production processes, reduce waste, and improve efficiency after implementing a consultant’s recommendations. A retail chain could optimize its store layout, improve customer service, and increase sales. The effectiveness hinges on the consultant’s expertise, the accuracy of their analysis, and the client’s commitment to implementing the recommended changes.
Pros:
- Expertise and Experience: Consultants bring specialized knowledge and a proven track record of success.
- Objective Perspective: Consultants provide an unbiased assessment of the organization’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Customized Solutions: Consultants develop solutions tailored to the specific needs of each business.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Consulting can lead to significant improvements in operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Agility and Adaptability: A well-designed organization is more responsive to changing market conditions.
Cons/Limitations:
- Cost: Consulting services can be expensive, particularly for small businesses.
- Implementation Challenges: Implementing organizational changes can be difficult and time-consuming.
- Dependence on Consultants: Organizations may become overly reliant on consultants, hindering their ability to solve problems independently.
- Lack of Internal Buy-In: If employees are not actively involved in the change process, they may resist the new organizational structure.
Ideal User Profile: Organizational design consulting is best suited for businesses that are experiencing significant growth, facing major challenges, or undergoing a strategic transformation. It is also beneficial for organizations that are seeking to improve their efficiency, agility, or innovation capabilities.
Key Alternatives (Briefly): Alternatives to consulting include internal organizational development teams or DIY approaches using online resources and frameworks. However, these alternatives may lack the expertise and objectivity of a professional consultant.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: Organizational design consulting can be a valuable investment for businesses that are committed to improving their performance. The key is to choose a reputable consulting firm with a proven track record and to actively engage in the change process. We recommend carefully evaluating your needs and selecting a consultant who has the expertise and experience to address your specific challenges.
Mastering the Art of Effective Organization
In summary, understanding the orgo definition and its implications is crucial for success in any endeavor. By embracing the principles of effective organization, businesses can improve their efficiency, agility, and innovation capabilities. The insights shared throughout this article underscore the importance of a well-defined structure, clear processes, and a culture that fosters collaboration and adaptability. Share your experiences with organizational design in the comments below, and let’s continue the conversation on how to build more effective and resilient organizations.