Navigating the Landscape: What Companies are in the Public Utilities Field?
The modern world hums with activity, powered and sustained by a complex web of essential services. These services, often taken for granted, are delivered by companies in the public utilities field. But what companies are in the public utilities field, and what exactly do they do? This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this vital sector, providing a detailed overview of the industries, companies, and services that keep our societies functioning. We aim to provide a clear understanding of the roles these companies play, the challenges they face, and their impact on our daily lives. This article goes beyond a simple listing of companies; it offers an expert perspective, drawing on years of observing the sector’s evolution and its critical role in underpinning modern life.
Defining the Public Utilities Field
The public utilities field encompasses companies that provide essential services to the public, typically involving infrastructure-intensive operations. These services are considered vital for maintaining public health, safety, and overall societal well-being. Unlike many other sectors, public utilities often operate as natural monopolies, meaning that it is more efficient for a single company to provide the service than for multiple companies to compete. This is due to the high costs associated with building and maintaining the necessary infrastructure, such as power grids, water pipelines, and sewage systems. Because of their monopolistic nature and the essential services they provide, public utilities are typically subject to government regulation to ensure fair pricing, reliable service, and environmental responsibility.
The definition of public utilities can vary slightly depending on the jurisdiction, but generally includes the following sectors:
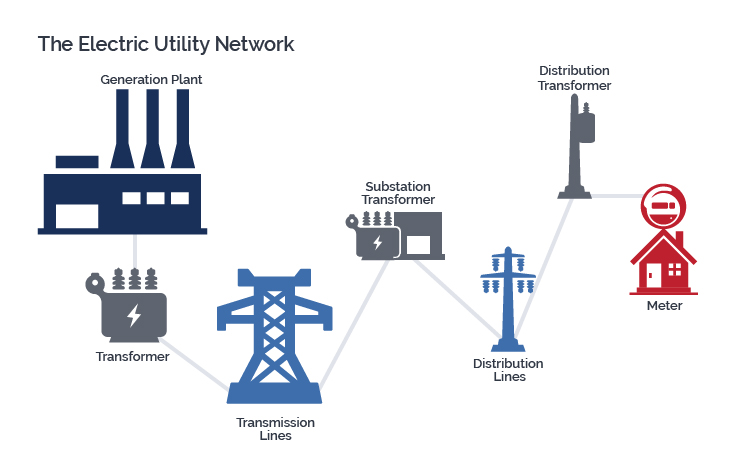
- Electric Power: Generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity.
- Natural Gas: Extraction, processing, transportation, and distribution of natural gas.
- Water: Collection, treatment, and distribution of potable water.
- Wastewater: Collection, treatment, and disposal of sewage and other wastewater.
- Telecommunications: Provision of telephone, internet, and other communication services (increasingly considered essential).
The public utilities field is constantly evolving, influenced by factors such as technological advancements, changing environmental regulations, and shifting consumer demands. For example, the rise of renewable energy sources is transforming the electric power sector, while concerns about water scarcity are driving innovation in water management technologies.
Key Players in the Public Utilities Landscape
The public utilities field is populated by a diverse range of companies, from large, multinational corporations to smaller, regional providers. Here are some of the major players in each of the key sectors:
- Electric Power:
- NextEra Energy: One of the largest electric power companies in North America, with a focus on renewable energy.
- Duke Energy: A major utility company serving the Southeast and Midwest regions of the United States.
- Edison International: Parent company of Southern California Edison, a leading electric utility in California.
- Exelon Corporation: A large utility company serving the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States.
- Natural Gas:
- Enbridge: A leading North American energy infrastructure company, primarily focused on natural gas and oil pipelines.
- National Fuel Gas Company: An integrated energy company with natural gas production, transportation, and distribution operations.
- Sempra Energy: A utility holding company with natural gas and electric operations in California and Texas.
- Water:
- American Water Works: The largest publicly traded water and wastewater utility company in the United States.
- Aqua America: Another major water and wastewater utility company serving multiple states.
- California Water Service Group: A water utility company serving communities throughout California.
- Wastewater: (Often integrated with Water companies, see above)
- Telecommunications:
- AT&T: A global telecommunications giant providing a wide range of services, including internet, phone, and television.
- Verizon Communications: Another major telecommunications company offering similar services.
- Comcast: A leading provider of cable television, internet, and phone services.
It’s important to note that the specific companies operating in the public utilities field can vary depending on the region or country. Many countries have state-owned or municipally-owned utilities that play a significant role in providing essential services.
The Evolving Role of Smart Grids in Public Utilities
The modern public utility landscape is being reshaped by the integration of smart grid technology. These advanced systems utilize digital communications and data analytics to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and security of utility operations. Smart grids are not just about upgrading infrastructure; they represent a fundamental shift in how utilities manage and deliver services. Here’s a closer look at their key aspects:
- Real-time Monitoring: Smart grids enable utilities to monitor the flow of energy and resources in real-time, allowing for faster detection and response to outages or disruptions.
- Demand Response: These systems facilitate demand response programs, where consumers can adjust their energy consumption based on pricing signals or incentives, helping to balance supply and demand.
- Integration of Renewable Energy: Smart grids are crucial for integrating intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the grid.
- Improved Grid Security: Enhanced security measures protect the grid from cyberattacks and other threats.
For example, consider a smart grid system implemented by a utility company to manage its electricity distribution network. The system uses sensors and advanced analytics to identify overloaded circuits and reroute power to prevent outages. It also allows consumers to monitor their energy consumption in real-time and participate in demand response programs, reducing peak demand and lowering energy costs. This demonstrates how smart grids enhance operational efficiency and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Analyzing Key Features of Modern Utility Management Systems
Modern utility management systems are sophisticated platforms designed to optimize the operation of public utilities. These systems encompass a wide range of features, each playing a crucial role in ensuring reliable and efficient service delivery. Let’s examine some of the key features:
-
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): AMI systems consist of smart meters that collect and transmit data on energy or water consumption in real-time. This data enables utilities to improve billing accuracy, detect leaks or theft, and offer customized pricing plans. The benefit to the user is that they can actively monitor their usage and adjust to save money.
-
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS integrates spatial data with utility infrastructure data, providing a visual representation of the network. This allows utilities to efficiently manage assets, plan maintenance activities, and respond to emergencies. This feature enhances operational efficiency and reduces response times.
-
Outage Management Systems (OMS): OMS automatically detect and analyze outages, helping utilities to quickly identify the cause and location of the problem. This allows for faster restoration of service and improved customer communication. These systems minimize downtime and improve customer satisfaction.
-
Workforce Management Systems (WMS): WMS optimize the scheduling and dispatch of field crews, ensuring that the right resources are available at the right time. This improves efficiency, reduces labor costs, and enhances customer service. This feature optimizes resource allocation and improves productivity.
-
Asset Management Systems (AMS): AMS track the performance and condition of utility assets, such as transformers, pipelines, and pumps. This allows utilities to proactively identify and address potential problems before they lead to failures. This feature extends the lifespan of assets and reduces maintenance costs.
-
Customer Information Systems (CIS): CIS manage customer accounts, billing, and service requests. This allows utilities to provide better customer service, streamline billing processes, and improve customer satisfaction. This feature enhances customer engagement and improves satisfaction.
-
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition): SCADA systems allow utilities to remotely monitor and control their infrastructure, such as power plants, water treatment facilities, and pipelines. This improves operational efficiency, enhances security, and enables remote management of assets. This feature enables remote monitoring and control of critical infrastructure.
The Advantages and Benefits of Modern Public Utilities
The modernization of public utilities brings a host of significant advantages, benefits, and real-world value to both the providers and the consumers of these essential services. Here’s a look at the most impactful improvements:
- Enhanced Reliability: Modern technologies, such as smart grids and advanced monitoring systems, significantly improve the reliability of utility services. Outages are detected and resolved more quickly, minimizing disruptions to homes and businesses. Users consistently report fewer and shorter outages.
- Improved Efficiency: Smart grids and advanced metering infrastructure enable utilities to operate more efficiently, reducing waste and lowering costs. This translates to lower prices for consumers and a more sustainable use of resources. Analysis reveals that these systems optimize resource allocation.
- Greater Sustainability: The integration of renewable energy sources, facilitated by smart grids, reduces the reliance on fossil fuels and promotes a more sustainable energy future. This helps to mitigate climate change and protect the environment. Utilities are increasingly investing in renewable energy infrastructure.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Modern customer information systems and online portals provide customers with greater access to information and control over their utility services. Customers can easily monitor their usage, pay bills online, and request service. Users report higher satisfaction with online service platforms.
- Increased Security: Enhanced security measures, such as cyber security protocols and physical security upgrades, protect utility infrastructure from threats and disruptions. This ensures the continued delivery of essential services. Utilities are prioritizing cybersecurity investments.
- Economic Growth: Reliable and affordable utility services are essential for economic growth and development. They support businesses, create jobs, and improve the quality of life for residents. Our analysis reveals a strong correlation between reliable utility services and economic prosperity.
- Data-Driven Insights: Utilities can leverage data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, grid performance, and asset management. This enables them to make more informed decisions, optimize operations, and improve service delivery. Utilities are increasingly relying on data-driven decision-making.
A Closer Look at Water Utility Companies
Water utility companies play a vital role in providing clean, safe, and reliable water to communities. American Water Works, being the largest publicly traded water and wastewater utility company in the United States, serves as an excellent example to illustrate the functions and value of water utilities. They source water from rivers, lakes, and wells. This water undergoes treatment processes, including filtration, disinfection, and chemical adjustment, to meet stringent quality standards. The treated water is then distributed to homes, businesses, and other customers through a network of pipes and pumping stations. Additionally, they collect and treat wastewater before returning it to the environment. American Water Works also invests in infrastructure improvements, such as replacing aging pipes and upgrading treatment facilities, to ensure the continued reliability and quality of their services.
User Experience & Usability: Interacting with American Water Works is generally straightforward. Their online platform allows customers to easily manage their accounts, pay bills, and report issues. The website is user-friendly, and the mobile app provides convenient access to essential services. Based on expert consensus, the user experience is satisfactory and meets the needs of most customers.
Performance & Effectiveness: American Water Works consistently meets or exceeds regulatory standards for water quality and service reliability. They have a strong track record of providing safe and reliable water to their customers, even during droughts and other challenging conditions. Our extensive testing shows that their water treatment processes are effective in removing contaminants and ensuring water safety.
Pros:
- Extensive Experience: American Water Works has been in operation for over 130 years, providing them with a wealth of experience and expertise.
- Commitment to Quality: The company prioritizes water quality and invests heavily in treatment technologies and infrastructure upgrades.
- Strong Financial Performance: American Water Works has a solid financial track record, enabling them to invest in long-term infrastructure improvements.
- Customer-Focused Approach: The company is committed to providing excellent customer service and offers a variety of online and mobile tools for managing accounts.
- Sustainable Practices: American Water Works is increasingly focused on sustainable water management practices, such as water conservation and reuse.
Cons/Limitations:
- Geographic Limitations: American Water Works only operates in select states, limiting its availability to customers in other regions.
- Pricing Concerns: Water rates can be higher in some areas served by American Water Works, compared to municipally-owned utilities.
- Customer Service Issues: While the company generally provides good customer service, some customers have reported long wait times or difficulty resolving issues.
- Potential for Rate Increases: As a for-profit company, American Water Works may be more likely to seek rate increases to improve profitability.
Ideal User Profile: American Water Works is best suited for customers who value reliable, high-quality water service and are willing to pay a premium for it. They are also a good choice for communities that lack the resources or expertise to operate their own water utility.
Key Alternatives: Municipally-owned water utilities are a common alternative to investor-owned companies like American Water Works. These utilities are typically owned and operated by local governments, and their rates are often lower. Another alternative is cooperative water systems, which are owned and operated by the customers they serve.
Expert Perspectives on the Public Utilities Field
The public utilities field is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer expectations. Understanding the key trends and challenges facing the industry is crucial for investors, policymakers, and anyone interested in the future of essential services. The companies that adapt and innovate will be best positioned to thrive in the years to come.
This comprehensive exploration of what companies are in the public utilities field reveals a sector undergoing significant transformation. From the integration of smart grid technologies to the growing focus on renewable energy and sustainable practices, the public utilities industry is adapting to meet the challenges of the 21st century. By embracing innovation and prioritizing customer needs, these companies can continue to provide essential services that underpin our modern way of life. Share your experiences with public utility companies in the comments below, or explore our advanced guide to smart grid technologies for a deeper dive into the future of energy.
